In today’s digital age, data privacy is of utmost importance. With the increasing amount of personal information being collected and processed, it’s crucial to understand the methods used to protect individuals’ identities. Two terms that often come up in discussions about data protection are pseudonymization vs. anonymization. In this article, we will explore these concepts, providing practical examples to help you better understand their significance.
Table of Contents
Introduction
In our increasingly data-driven world, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. Pseudonymization and anonymization are two techniques used to protect data and maintain privacy. They may sound similar, but they serve distinct purposes and have different implications. Let’s explore them in detail.
Explaining Pseudonymization
What Is Pseudonymization?
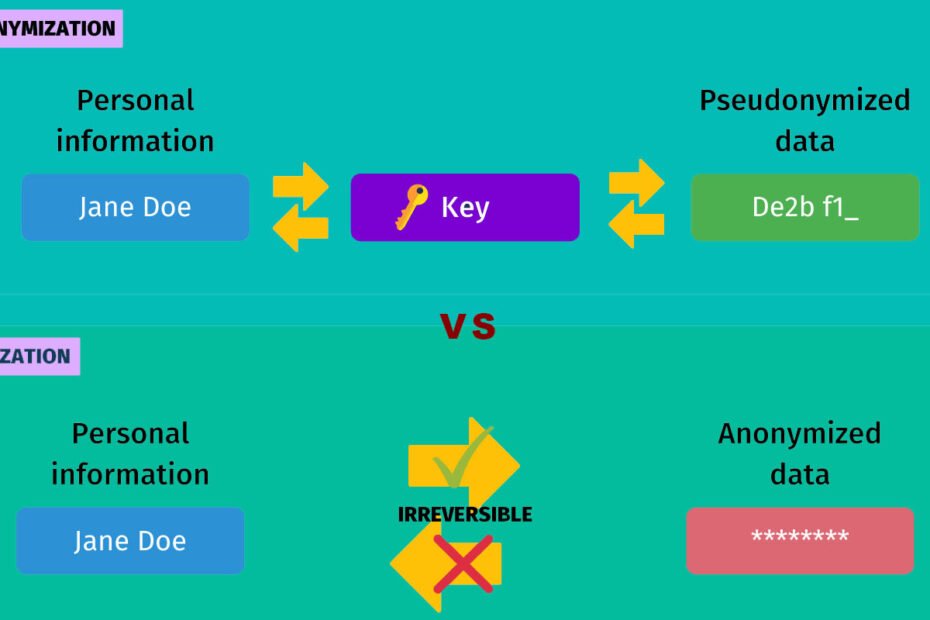
Pseudonymization is a data protection technique that replaces or masks personally identifiable information (PII) with pseudonyms. Pseudonyms are unique identifiers that allow data to be linked back to the original individual, but only if certain conditions are met.
How Does Pseudonymization Work?
In pseudonymization, PII such as names, email addresses, or social security numbers is replaced with codes or tokens. These tokens are kept in a separate location, ensuring that even if the data is breached, it remains useless to unauthorized users without access to the pseudonymization key.
Practical Example of Pseudonymization
Imagine a healthcare database. Instead of storing patients names and addresses, the system assigns each patient a unique identification number. This number along with the patient’s medical data, is stored in the database. If necessary authorized personnel can use the identification number to link the data back to the patient.
Methodology
Pseudonymization strategies commonly include:
- Tokenization: Replacing identifying information with randomly generated tokens.
- Encryption: Applying cryptographic techniques to protect personal data.
- Hashing: Creating fixed-length representations of data for identification purposes.
Key Benefits
- Data utility preservation: Pseudonymization maintains the usefulness of data for authorized processes.
- Granular access control: It enables restricted access to sensitive information while allowing authorized users to work with pseudonyms.
- Enhanced security: By dissociating identifiers from the data, the risk of unauthorized re-identification is significantly reduced.
Explaining Anonymization
What Is Anonymization?
Anonymization, on the other hand, takes data protection a step further. It aims to make data entirely anonymous, rendering it impossible to link it back to any individual.
How Does Anonymization Work?
Anonymization methods include removing or aggregating data to the extent that individual identities cannot be deduced, even with additional information. Unlike pseudonymization, there is no key that can reverse the process.
Practical Example of Anonymization
Consider a survey where respondents’ ages are recorded. Anonymizing this data might involve grouping the ages into broad categories like “under 18,” “18-30,” “31-45,” and so on, making it impossible to determine the exact age of any respondent.
Methodology
Anonymization typically involves various methods, including but not limited to:
- Data aggregation: Combining multiple data points to obscure individual identities.
- Generalization: Replacing specific values with broader categories.
- Noise injection: Adding random data to mask sensitive information.
- Data perturbation: Slight modification of data values to prevent re-identification.
Key Benefits
- Compliance with data protection regulations: Anonymized data often falls outside the scope of data protection regulations, reducing legal constraints.
- Enhanced data sharing: Organizations can share anonymized data more freely, fostering collaboration and research.
- Mitigation of privacy risks: Anonymization minimizes the risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
Key Differences Between Pseudonymization vs. Anonymization

Level of Reversibility
- Pseudonymization is reversible with the proper key, while anonymization is irreversible.
Use Cases
- Pseudonymization is often used when data needs to be linked to individuals for legitimate purposes, like medical research.
- Anonymization is preferred when complete data anonymity is necessary, such as in public surveys.
Data Utility
- Pseudonymized data retains some utility since it can be re-identified if needed.
- Anonymized data sacrifices utility for the sake of privacy.
Legal Implications
- Pseudonymization may still fall under certain data protection regulations, as it retains some link to individuals.
- Anonymization often offers greater legal protection, as it completely removes the risk of identification.
Table Comparison Anonymization vs. Pseudonymization
Let’s highlight some key distinctions between these two data protection methods:
| Aspect | Anonymization | Pseudonymization |
|---|---|---|
| Reversibility | Irreversible | Potentially reversible (with the right key) |
| Data usability | Reduced, as data is often aggregated | Maintained, with the use of pseudonyms |
| Legal implications | Less stringent regulations may apply | Subject to data protection laws |
| Use cases | High privacy, less usability | Balancing privacy and data utility |
When to Use Pseudonymization and When to Use Anonymization
The choice between pseudonymization and anonymization depends on the specific data use case and privacy requirements. It’s essential to assess the level of protection needed and the potential utility of the data.
Challenges and Considerations
Data Quality
Maintaining data quality can be challenging with pseudonymization and anonymization techniques. Careful planning and validation are necessary to ensure the data remains useful.
Re-identification Risks
Both pseudonymized and anonymized data can still be vulnerable to re-identification attacks, emphasizing the importance of robust security measures.
Best Practices
Combining Pseudonymization and Anonymization
In some cases, combining both techniques can offer a balance between privacy and data utility. This approach provides an added layer of protection.
Regular Data Auditing
Periodic audits of pseudonymized or anonymized data can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure ongoing compliance with data protection regulations.
Pseudonymization vs. Anonymization Under GDPR
let’s delve into how anonymization and pseudonymization relate to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a comprehensive privacy regulation that sets strict standards for the protection of personal data within the European Union (EU).
Anonymization under GDPR
Under the GDPR, anonymization is considered one of the most effective ways to process personal data while ensuring compliance with the regulation. When data is truly anonymized, it is no longer considered “personal data” under the GDPR’s definition. This means that the data subject (the person to whom the data belongs) cannot be identified directly or indirectly, and the data falls outside the scope of the GDPR’s strict requirements.
Key Points:
- Anonymized data is not subject to GDPR regulations, such as the need for explicit consent or the right to erasure.
- Anonymization is a powerful method for organizations to handle data without the burden of GDPR compliance.
- However, the anonymization process must be irreversible and robust to prevent re-identification.
Pseudonymization under GDPR
Pseudonymization, while not providing the same level of data anonymity as anonymization, still plays a significant role in GDPR compliance. It allows organizations to separate personal data from identifiers, replacing direct identifiers (such as names or email addresses) with pseudonyms (randomly generated tokens or codes). This process helps protect the privacy of data subjects and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Key Points:
- Pseudonymization allows organizations to retain some level of data utility while complying with GDPR.
- While pseudonymized data is still considered personal data under GDPR, it is subject to fewer regulatory requirements.
- GDPR acknowledges pseudonymization as a security measure that can reduce data breach risks and enhance data protection.
GDPR’s Perspective
It’s essential to note that GDPR encourages the use of both anonymization and pseudonymization as part of a broader data protection strategy. The regulation recognizes that these techniques can help organizations strike a balance between data utility and privacy.
Moreover, GDPR emphasizes the importance of implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to safeguard personal data. Anonymization and pseudonymization are considered such measures, and organizations are encouraged to adopt them as part of their data protection practices.
Conclusion
In an era where data is a valuable asset, understanding the difference between pseudonymization and anonymization is crucial. These techniques play a pivotal role in protecting individuals’ privacy while allowing for legitimate data use. By choosing the right method and implementing best practices, organizations can strike a balance between data utility and privacy.
By understanding the disparities between these techniques, you can ensure that your data handling practices align with privacy regulations while still meeting your business objectives. Remember that data privacy is not a one-size-fits-all approach, and tailoring your strategy to your unique circumstances is key to success in today’s data-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is pseudonymization more secure than anonymization?
- Pseudonymization offers some level of reversibility, making it less secure in terms of complete anonymity. Anonymization is generally considered more secure for privacy protection.
- Can pseudonymized data still be used for research purposes?
- Yes, pseudonymized data can be used for research, as it allows for data linkage while protecting individual identities.
- What are the legal implications of pseudonymization and anonymization?
- Pseudonymization may still be subject to data protection regulations, while anonymization often provides stronger legal protection due to its irreversible nature.
- Are there any industry-specific guidelines for data pseudonymization and anonymization?
- Yes, some industries have specific guidelines and regulations for data protection, which may include recommendations for pseudonymization and anonymization practices.
- How often should data audits be conducted for pseudonymized or anonymized data?
- Regular data audits are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with data protection regulations. The frequency of audits may vary depending on the nature of the data and regulatory requirements.