Data masking best practices mean hiding important data by: Identify PII, Classify the data, choose the right technique, Keep it realistic, and Regularly update.
Learn Data Masking Best Practices and get real-world examples to safeguard your sensitive information effectively. Explore how data masking can enhance your data security measures:
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s digital age, the security of sensitive data is of paramount importance. With cyber threats on the rise, it’s crucial to implement robust data security measures. Data masking, often referred to as data obfuscation, is one such practice that ensures sensitive information remains hidden and protected. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into data masking best practices, providing you with real-world examples to help you understand how to safeguard your critical data effectively.
Understanding Data Masking
Data masking is a process where original data is transformed into a fictitious but realistic version, making it impossible to trace back to the original data source. This technique helps in preserving data privacy while allowing organizations to use the information for testing, analytics, and other non-production purposes.
Types of Data Masking
Data masking comes in various forms, each catering to specific needs. Here are the three basic types:
- Static Data Masking: Static data masking involves creating a duplicate version of a dataset and replacing sensitive data at rest. It is used for providing realistic, high-quality data to support application development.
- Dynamic Data Masking: Dynamic data masking alters sensitive data in production datasets in real-time. It ensures that only authorized users access the original data, while non-authorized users can view only masked data.
- On-the-fly Data Masking: Inflight data masking modifies sensitive information as it moves from one environment to another, to ensure that sensitive data is protected before it reaches its destination. Inflight data masking is particularly valuable for organizations that are migrating between systems (legacy application modernization, for instance), or maintaining continuous integration of different datasets.
Data Masking Best Practices
To achieve maximum effectiveness, organizations should consider these best practices when implementing data masking:
- Identify Sensitive Data: Begin by identifying what data needs to be masked.
- Data Classification: Categorize data based on its sensitivity to determine the level of masking required.
- Secure Masking Algorithms: Ensure that the chosen masking techniques are secure and effective.
- Testing and Validation: Regularly test and validate the masked data to ensure it remains useful.
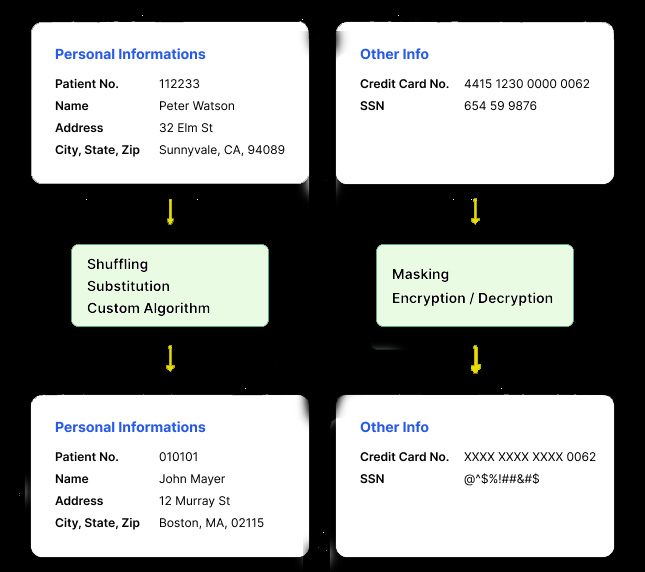
Let’s explore the data masking best practices in detail:
1. Identify Sensitive Data
Before applying data masking techniques, it’s essential to identify what data is sensitive. This includes personal information, financial data, and any confidential business information. By pinpointing this critical data, you can prioritize its protection.
Before you can protect your sensitive data, you need to understand what data you have and its varying degrees of sensitivity. You need to know where it is, who can access it, where it moves, and when. You’ll need to map out:
- Where sensitive data is stored and used (in both production and non-production environments)
- Who is authorized to view it
- What these users use it for
2. Data Classification
Classify your data into different categories based on sensitivity. For instance, you may have data that is highly confidential and data that is less critical. Tailor your data masking approach accordingly.
3. Choose the Right Data Masking Technique
Once you know where your sensitive data is and the circumstances in which the data is stored and used, you can define which data masking techniques are needed. It’s important to recognize that data masking techniques will likely vary across the enterprise, depending on the type of data being protected, internal security policies, usage needs, and budgetary requirements. There are various data masking techniques available, including substitution, shuffling, and encryption. Select the technique that aligns best with your data security requirements.
Data masking employs several techniques to protect sensitive information:
- Substitution: In substitution, original data is replaced with fictitious data that resembles the real data in structure but doesn’t reveal any sensitive details. For example, a social security number “123-45-6789” could be substituted with “XXX-XX-XXXX”.
- Shuffling: Shuffling involves rearranging data so that the relationships between elements are retained, but the original data is hidden. For instance, a list of customer addresses could be shuffled, so they are still in the same order but do not correspond to the correct customers.
- Encryption: Data encryption transforms sensitive data into an unreadable format, which can only be decrypted by authorized users. For example, a credit card number “1234 5678 9012 3456” would be encrypted into a series of seemingly random characters.
- Nulling: Nulling simply replaces sensitive data with null values, rendering it unreadable. A date of birth “01/15/1980” might be nullified to “null” or “01/01/0000”.
4. Maintain Data Realism
While obfuscating data, ensure that the masked data retains its realism. If the data does not appear realistic, it may hinder testing and analysis processes. Consistency is key when applying data masking. Make sure the same data consistently appears masked in all test environments.
5. Regularly Update Masked Data
As your data changes, your masked data should evolve as well. Regularly update masked data to ensure it remains current and applicable.
Implement robust auditing and monitoring systems to track any breaches or unauthorized access to your masked data.
6. Access Control
Control access to the original data and the masked data. Not everyone in your organization needs access to the original data, so limit permissions accordingly.
Real-World Examples
To better understand these best practices, let’s look at some real-world examples:
Example 1: Customer Database
Suppose you run an e-commerce business with a vast customer database. To ensure the protection of customer data, you employ data masking. Personal details such as names, addresses, and credit card numbers are replaced with fictitious but realistic data. This allows you to carry out testing and analysis without risking customer information.
Example 2: Healthcare Records
In the healthcare industry, patient confidentiality is paramount. By applying data masking, patient records are altered to protect identities while retaining the information’s usefulness for research and analysis.
The Importance of Data Masking
- Protecting Sensitive Information: Data masking is essential for safeguarding sensitive data. By disguising the information, it becomes inaccessible to unauthorized users, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Compliance with Regulations: Various regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, require organizations to protect sensitive information. Data masking helps organizations comply with these regulations.
- Preserving Data Utility: Data masking ensures that sensitive data remains useful for testing, development, or analytical purposes, without exposing actual, sensitive details.
Benefits of Data Masking
- Enhanced Security: Data masking significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, enhancing the overall security of sensitive information.
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements is simplified when data masking is employed, reducing the potential for fines or legal consequences.
- Cost Savings: By protecting sensitive data, organizations save money that would otherwise be spent on breach recovery and reputation management.
Data Masking vs. Data Encryption
While data masking focuses on data obfuscation, data encryption converts data into an unreadable format. Both are vital, but they serve different purposes. Data masking allows for the use of data, while data encryption secures data at rest and in transit.
FAQs
What is data masking?
Data masking, also known as data obfuscation, is a technique used to protect sensitive data by replacing it with fictitious but realistic information, making it impossible to trace back to the original data.
How does data masking benefit organizations?
Data masking allows organizations to use sensitive data for testing, analytics, and other non-production purposes without compromising data security and privacy.
Can data masking be applied to different types of data?
Yes, data masking can be applied to various types of data, including personal information, financial data, and confidential business information.
What are the common data masking techniques?
Common data masking techniques include substitution, shuffling, and encryption, each serving different data security needs.
Is data masking a one-time process?
No, data masking is an ongoing process that requires regular updates to ensure masked data remains current and applicable.
How does data masking help in regulatory compliance?
Data masking aids in compliance with data protection regulations by safeguarding sensitive information, reducing the risk of data breaches, and ensuring privacy.
How can data masking benefit my organization?
- Data masking enhances security, ensures compliance, and saves costs associated with data breaches.
Are there specific regulations that require data masking?
- Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA often require data masking to protect sensitive information.
What are the common challenges in implementing data masking?
- Challenges include maintaining data integrity and ensuring the masked data remains usable.
Is data masking a one-time process?
- No, data masking requires continuous monitoring and adjustment to adapt to evolving security threats and changing data usage patterns.
Conclusion
Data masking is a crucial practice in safeguarding sensitive information in today’s data-driven world. By implementing the best practices discussed in this article, you can protect your data effectively and maintain the privacy and security of your customers and organization. Remember, the key to successful data masking lies in identifying sensitive data, choosing the right masking techniques, and regularly updating your masked data. Stay secure and stay informed.

